Carbanion
source : slide player.com
Carbanion –
When a covalent bond , in which Carbon is attached to a lesser electro negative atom , breaks up by heterolytic fission. Thus carbon-atom acquires a negative charge due to an extra electron.

“Organic ions containing a negatively charged carbon-atom are called carbanions”
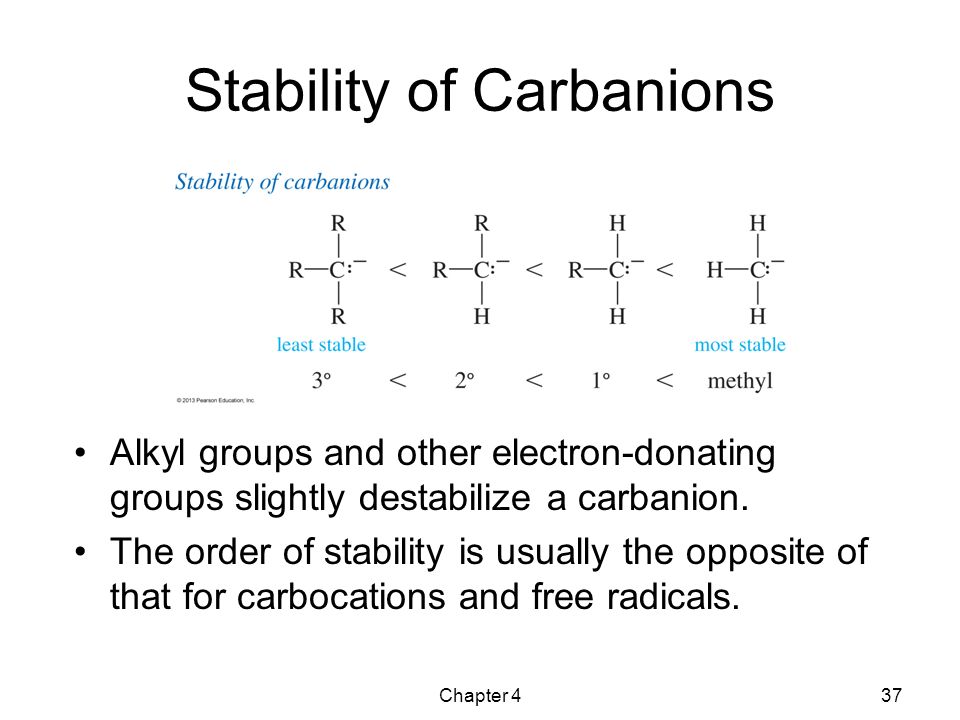
These are named after the parent alkyl group & adding the word carbanion .These are also termed as Primary, Secondary & Tertiary, depending upon the nature of carbon-atom bearing negative charge

Characteristics –
1) Its Carbon-atom contains negative charge .
2) The valence shell of negatively charged Carbon-atom contains 8-electrons. Thus its octet is complete & it contains a lone pair of electron .
3) The negatively charged carbon is in a state of sp3 hybridization .The hybrid orbitals are directed towards the corners of a tetrahedron. Three of the hybrid orbitals are involved in the formation of single covalent bonds with other atoms while the IVth hybrid orbital contains a lone pair of electron. Thus it has a pyramidal structure similar to NH3 molecule.
4) Its carbon contains eight electrons even they are highly reactive intermediate.
5) They are readily attacked by electrophillic reagents.
6) Carbanion is itself a nucliophile
7) The order of stability is-
![]()
8) The stability of carbanion is influenced by resonance . Acetonyl & benzyl carbanions possess resonance & thus extra stable.