CIP rule

source : Chemistry Libre Texts
CIP rule-
The Cahn- Ingold – Prelog (CIP) sequence rules, named for Robert Sidney Cahn, Crystopher Kelk Ingold & Vladimir Prelog -alternatively known as CIP Rule. The purpose of CIP priority rule is to name a specific stereoisomer of a molecule. Stereoisomers are compounds having same molecular formula and same connectivity of atoms but differ in their three dimentional orientation.
The configuration of the chiral carbon is decided as follow-
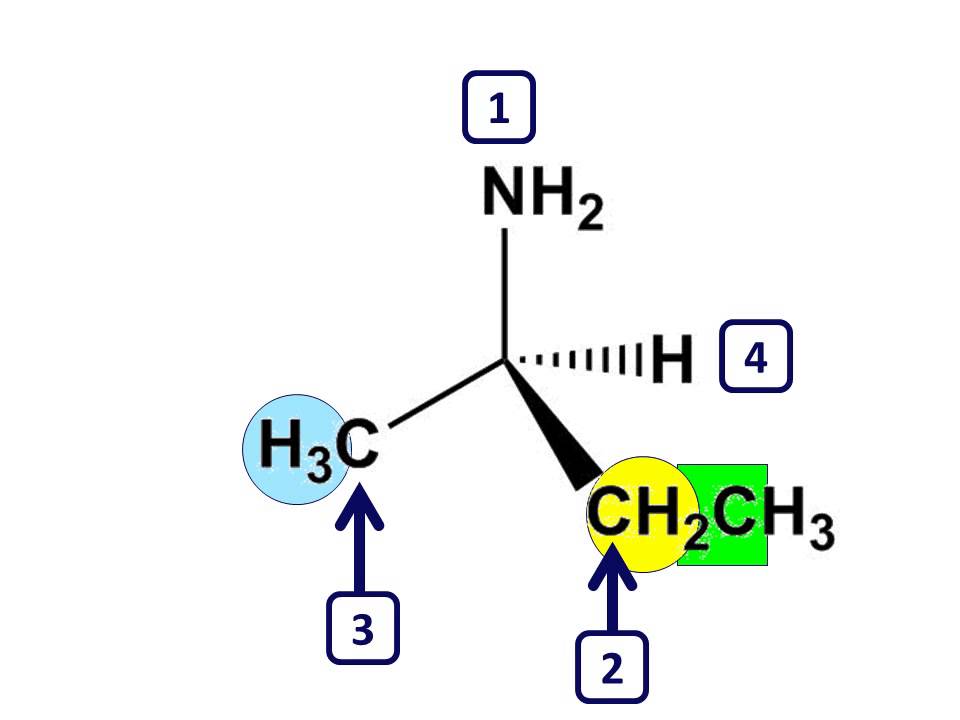
The four atoms or groups attached to the chiral carbon are ranked in order of priority , priority is decided by following sequence rules.
(a) Atom of higher atomic number gets priority. Atom of higher priority is assigned no.1 & atom of least priority is assigned no.4.
I>Br>Cl>O>N>C>H
decreasing priority

source : wikipedia
(b) If the first atom is the two groups have same atomic number then relative priority of the group is decided by a comparison of the atomic number of the next atom in the two groups.
Ex.1—- In CH3 & –CH2–CH3

In both first atom is Carbon but next atom in –– CH 3 is H , while in ––CH2––CH3 , next atom is ‘C’. So ethyl group is given higher priority than methyl group.
Ex.2 — –CHO is given higher priority than –CN because in group  , C is directly attached to oxygen while in –CN group C is directly attached to N. (at. no. of oxygen is greater than N).
, C is directly attached to oxygen while in –CN group C is directly attached to N. (at. no. of oxygen is greater than N).
(c) Multiple bonds are treated as separate single bonds.
Ex.1—- –CH=O is given priority over –CH2OH
I>Br>Cl, OH>NO2>NH2>COOH>CHO>CH2OH
Examples Of CIP rule –

source : Study.com

source : schoolbag.info

source : OChemPal

source : Chemistry for everyone-wordpress.com