Distribution Law or Partition Law

Partition Law or Distribution Law
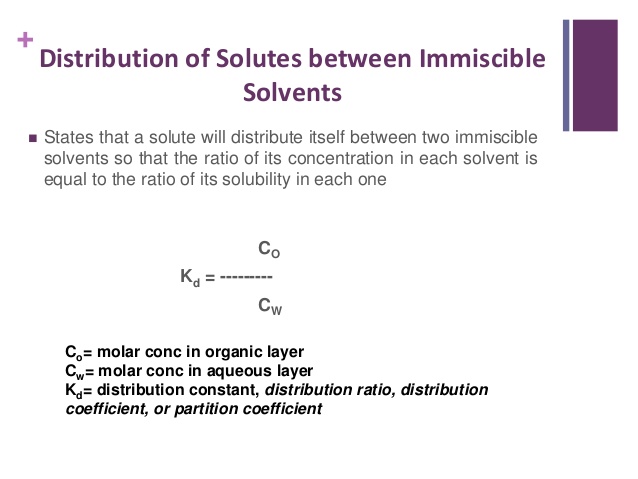
This Law was given by Nernst. This law gives the relationship between the concentration of a given substance in two different phases in equilibrium with each other.
Suppose, if a small quantity of solute soluble in both the liquids is added then solute distributes it self in two liquid & equilibrium is set up. Both the liquids must be immiscible with each other If the concentration of the solute in two liquids are C1 & C2. According to this law,
C1/C2=K (constt.)
k= distribution or partition coefficient
Factors affecting Distribution Coefficient-
- The value of K depends upon the temperature , nature of solute , nature of two solvents .
- It does not depend upon the amount of solute or solvents taken.
If the solubilities of given solute in the two solvents at the given temperature are S1 & S2 respectively, then
C1/C2 = S1/S2 =K
Ex. Water & ether are immiscible with each other. Solute succinic acid is soluble in both of these solvents. If small amount of succinic acid is added in a mixture . Then,
Concentration of succinic acid in water = Cwater
Concentration of succinic acid in ether = Cether
K = Cwater / Cether
C water is more than Cether so C water is taken in the numerator & C ether in the denominator.
Experimental Verification
For experimental verification of distribution law, different quantity of the solute are added in different quantities of two solvents in many experiments . If the value of distribution coefficient for each experiment remains the same. This shows that the data follows distribution law.
Conditions for Distribution Law
- Both the solvents must be immiscible with each other
- It is applicable only for dilute solution
- Temperature remains constant throughout the experiment.
- The molecular state of the solute in the two solvents should be the same.
Applications of Distribution Law
- Determination of Solubility The values of K is equal to the ratio of solubilities of the solute in the two solvents.
K =C1/ C2 = S1/ S2
If value of K & solubility of the solute in one solvent is known then we can calculate the solubility of solute in other solvent.
- Solvent Extraction. Extraction of one substance from a solution containing various substances by using a suitable solvent is known as solvent extraction.
“The amount of extracted substance is more if smaller amount of solvent are used many times rather than using larger amount of solvent a fewer times”.