First order reaction-

source : askIITians
First order reaction-
” A first order reaction is that in which the rate of reaction is determined by the change of one concentration term of reactant only.”
Ex.1) Inversion of cane sugar-
C12 H22 O11 + H2O ————> C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
Rate = K [C12 H22 O11]
Ex.2) Decomposition of nitrogen penta oxide-
N2O5 (g) ——– > 2 NO2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
Rate = K [N2O5]
Ex.3) Decomposition of ammonium nitrite in aqueous solution –
NH4NO2 ——– > N2 (g) + 2 H2O
Rate = K [NH4NO2]
Consider the reaction,
A ————-> B + C
initial conc. a 0 0
conc. after’t’ time a- x x x
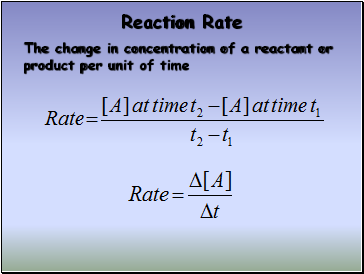
Rate = dx / dt = K[A] n
n = 1
dx / dt = K[A]
‘K ‘ is rate constant or velocity constant
dx / dt = K ( a- x)
dx /(a- x) = K.dt
Taking integration of both sides,
∫ dx /(a- x) = K ∫ dt
– ln( a- x) = Kt + C ———- eq. 1
C = integration constant
If t = 0 then x = 0
– ln( a- 0) = K x 0 + C
-ln a = C ——— eq.2
Putting the value of ‘C’ from eq.2 to eq. 1
– ln( a- x) = Kt – ln a
ln a – ln( a- x) = Kt
K = 1/ t [ ln a / (a- x)]
K = 2.303/ t [ log a / (a- x)]
If log [a / (a-x)] is plotted against ‘t’, then a straight line passing through the origin is obtained and slope is ‘ 2.303/ K’.
Characteristics of first order reaction –
1) Unit of ‘K’-
K = 2.303/ t [ log a / (a- x)]
unit of ‘K’ = 1 / time ( mole litre-1 / mole litre-1 )
unit of ‘K’ = time-1.
Time may be in hour , minute or second etc.
unit of ‘K’ = hour-1 or minute -1 or second -1
2) The unit of velocity constant is independent of the units of concentration because,
unit of ‘K’ = time-1
3) The time taken to complete a half reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
K = 2.303/ t [ log a / (a- x)]
If t = t1/2 then x = a/2
K = 2.303/ t1/2 [ log a / (a- a/2)]
K = 2.303/ t1/2 [ log a / ( a/2)]
K = 2.303/ t1/2 [ log 2]
K = 2.303/ t1/2 [ 0.3010]
K = 2.303 x 0.3010 / t 1/2
t1/2 = 0.693 / K