Pinacol-Pinacolone Rearrangement

source : you tube.com
Conversion of 1,2-glycols(pinacol) to ketone or aldehyde(pinacolone) by means of acid is called pinacol-pinacolone rearrangement.


Mechanism-This rearrangement is acid-catalysed reaction for ∝-glycols.Its mechanism is as follows-


Note:Migration of alkyl group and elimination of -OH by the proton catalyst take place simultaneously.
Main features of Pinacol-Pinacolone Rearrangement–
1.Stability of the carbonium ion–
when two -OH groups are different then -OH group will be removed which products more stable carbonium ion.
Example:

2.Migratory aptitude of the group-
a) The migrating group may be alkyl,aryl or even hydrogen atom,then migrating atom is Hydrogen atom.
Example1:
Example2:

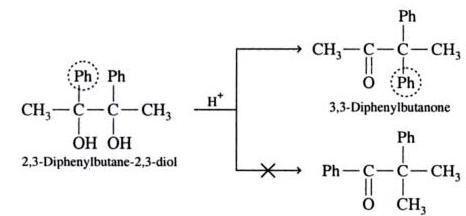
b)When each of the carbonatoms of glycol has an alkyl and an aryl group,then preferentially aryl group migrates.
Example:
c)When one carbon atom possesses two alkyl group and other aryl group then alkyl group migrates to form more stable carbonium ion.
Example:
d)When two aryl groups are present then migratory aptitude follows the order
p-anisyl>p-tolyl>phenyl>p-chlorophenyl
Example:

3)Intramolecular migration:
The migrating group migrates within the molecule.When a mixture of two different pinacols are heated in the present of acid , no cross product is formed.
4)Steric effect-The migration of the group is affected by steric factors.
Example:
5)Transmigration– The migrating group migrates to the trans side of the leaving group.