Buffer solution
source : slide share.net
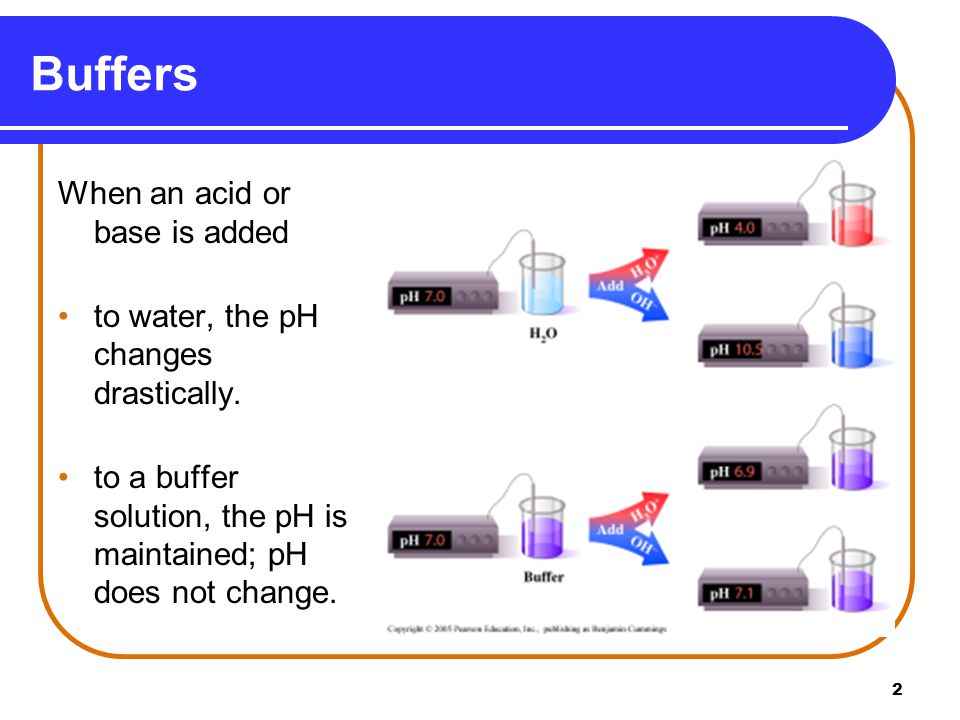
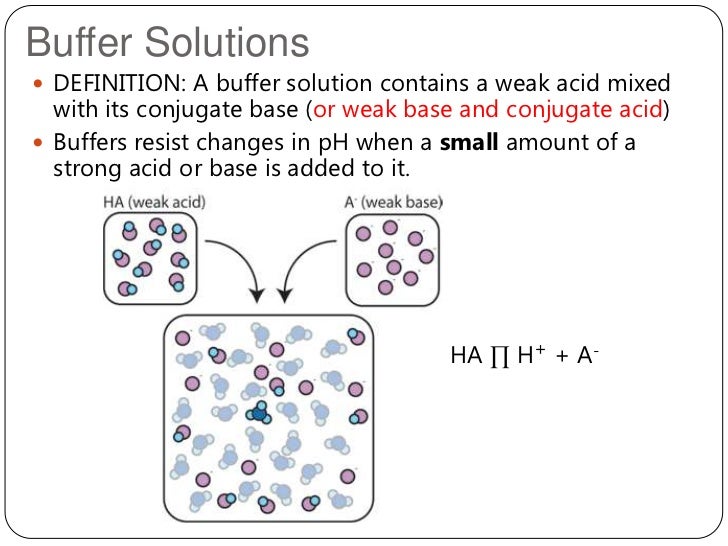
BUFFER SOLUTION
” A soln that resists a change in its pH on addition of small amount of acid or base or on dilution, is known as buffer soln”
Characteristics-
(i) It has a definite pH i.e. it has reserve acidity or alkalinity
(ii) Its pH does’t change on standing for long time.
(iii) Its pH does not change on dilution
(iv) Its pH is slightly changed or not changed by the addition of small amt. of an acid or base.
Buffer Solution are of two types-
(i) Acidic Buffer
An acidic buffer solution is obtained by dissolving a weak acid & salt of weak acid with strong base in water
Ex. H2CO3+NaHCO3
CH3COOH +CH3COONa /CH3COOK
(Acetic Acid+Na -Acetate / Pot. acetate)
HCN+ NaCN/KCN
Citric acid + Sodium Citrate
HCOOH + HCOOK
Formic acid + Pot. formate
Basic Buffer
A basic buffer Solution is obtained by dissolving a weak base & salt of weak base with strong acid in water
Ex. NH4OH+NH4Cl, NH4OH+(NH4)2SO4
Buffer action of acidic buffer Soln
It is explained by taking the example of buffer soln of acetic acid & Na-Acetate. Sodium Acetate is a strong electrolyte & ionises as follows-
CH3COONa —->CH3COO +Na+ (Completely ionise)
Acetic Acid is a weak electrolyte & ionises as follows
CH3COOH —–>CH3COO +Na+
(Partially ionise)
When small amt of HCl is added to the Solution, then H+ obtained from HCl combine with acetate ion to form CH3COOH which is partially ionised, thus the concentration of H+ & pH-value remains almost unchanged.
HCl——> H++Cl–
CH3COO–+H+ ——> CH3COOH
from
S. Acid
when small amt. of NaOH is a added to the Soln, then OH– obtained from NaOH combine with CH3COOH to form water. Therefore the concentration of OH– & pH remains almost unchanged.
NaOH —–>Na+ + OH–
CH3COOH+OH– —–> CH3COO–+H2O
Buffer Action of Basic Buffer Solution
Buffer action of basic buffer soln can be explained by taking the example of buffer soln of NH4OH & NH4Cl. NH4Cl is a strong electrolyte & completely ionises as follows-
NH4Cl —–> NH4++Cl–
NH4OH is weak electrolyte hence partially ionises
NH4OH —–> NH4+ + OH–
when small and of HCl is added then H+ obtained from acid reacts with NH4OH & water is formed. Thus the concentration of H+ & pH value remains almost uncharged.
HCl ——>H++Cl–
NH4OH + H+ ——> NH4+ + H2O
when small amt. of NaOH is added to the solution then OH– obtained from NaOH combine with NH4+ to form NH4OH therefore the concentration of OH– & pH remains almost unchanged.
NaOH ——> Na+ + OH–
NH4+ + OH– —–> NH4OH
(Weakly Ionised)
Calculation of pH of a buffer soln
Acidic Buffer Solution
[H+] = Ka [acid]/[salt]
pH = log 1/[H+]
Basic Buffer Solution
[OH-] = Kb [base]/[salt]
pOH = log 1/[OH-]
pH =14 -pOH
Numericals
Q – [Acetic acid]= 0.09 mole
[Na-acetate]= 1.5 mole
[H+] = Ka [acid]/[salt]
=1.8 x 10-5 [0.09/1.5]
=10.8 x 10-7
pH = –log[H+]
= –log 10.8×10–7
=–[log 10.8–7 log 10]
=–1.0334+7
pH= 5.97 Ans.
Q. Cal. the pH of that buffer solution which contain 5 gm. CH3COOH & 7.5 gm. Na– acetate in 500ml . Ka=1.8×10–5
Moles of Acid=w/m = 5/60=1/12
Moles of Salt=7.5/82 =0.091
[H+] = Ka [acid]/[salt]
=1.8 x 10-5 [(1/12) /0.091]
=1.65 x 10-5
pH = –log[H+]
= –log[ 1.65 x 10-5]
=–[log 1.65–5 log 10]
=–0.2175+5
pH= 4.7825 Ans.
Q. Calculate the pH of that buffer soln which is obtained by dissolving 0.2 mole of NH4OH & 0.25 mole of NH4Cl in water.
Kb=1.8×10–5
Ans . [base] =0.2
[salt]=0.25
[OH-] = Kb [base]/[salt]
=1.8 x 10-5 [0.2/0.25]
=1.44 x 10-5
pOH = – log [OH-]
=-log[1.44 x 10-5]
= -log 1.44+5 log 10
=-.1584 +5
pOH =4.842
pH =14 -pOH
=14-4.842
pH =9.158 Ans.
Q. Calculate the pH of that buffer solution which contain 5.25 gms. of NH4OH & 8.025 gm NH4Cl. Kb=1.8×10–5
Moles of base=w/m
= 5.25/35 =0.15
Moles of salt =8.025/53.5
=0.15
[OH-] = Kb [base]/[salt]
=1.8 x 10-5 x(0.15/0.15)
=1.8 x 10-5
pOH = log 1/[OH-]
=–log(1.8×10–5)
=-log 1.8+5 log 10
=- 0.2553 -5
pOH =4.7447
pH =14 -pOH
=14 – 4.7447
pH=9.2553 Ans.