acid base concept

chemwiki.ucdavis.edu
Arrhenius concept–
a) Acid – An acid is a substance which gives hydrogen ion (H+) in aqueous solution i.e. when dissolved in water
Ex. HCl –> H++Cl–
(aq.)
CH3COOH <—->CH3COO–+H+
(aq.)
KHSO4(aq.) –> K++H++ SO4––
b) Base – A base is a substance which gives hydroxide ion (OH–) in aqueous solution.
Ex. KOH(aq.) –> K++OH–
NH4OH(aq.) –> NH4+ +OH–
c) According to arrhenius concept acids & bases which ionises completely in aqueous solution are called strong acids & strong bases respectively.
Strong Acid HCl(aq.) –> H++Cl–
Weak Acid CH3COOH(aq.)<—-> CH3COO–+ H+
Strong Base NaOH (aq)–> Na++OH–
Weak Base NH4OH(aq.) –> NH4+ +OH–
d) Water is amphoteric because it gives both H+& OH– in solution
H2O –>H++OH–
Bronsted Lowry concept
a) Acid An acid is a substance (molecule or cation or anion) that gives proton i.e. H+ or acid is proton donor
HCl –> H++Cl–
HCO3– –> H++ CO3––
[Al(H2O)6]3+ –> H++[Al(H2O)5OH)2+
b) Base-A base is a substance (molecule or cation or anion) that accepts proton i.e.H+ or base is proton acceptor.
H2O+H+–>H3O+
CO3–– +H+ –>HCO3–
CN–+H+ –>HCN
c) Conjugate Acid-Base pair
Conjugate Acid- Chemical species, that is formed from the base by the gain of proton or H+
Base + H+ –>[Conjugate Acid]
Ex. H2O+H+ –>H3O+ (Conjugate Acid)
Conjugate Base-Chemical species that is formed from the acid by the loss of proton i.e H+
Acid –>H++[Conjugate base]
HCl–>H++Cl– (Conjugate base)
“A pair of acid & base which differ by a proton is called as conjugate Acid & base pair”
Example.1
NH3(aq.) +H2O(l) <—-> NH4+(Aq)+OH–
base1 acid2 acid1 base2
NH3(aq.) and NH4+(Aq) are conjugate acid base pair.
H2O(l) and OH– are conjugate acid base pair.
Example.2:
HCl + H2O <—-> H3O+ + Cl–
acid 1 base2 acid2 base1
HCl and Cl– are conjugate acid base pair.
H2O and H3O+ are conjugate acid base pair.
(d) Relative Strength of conjugate Acid -Base Pair – The conjugate base of strong acid is weak & conjugate acid of strong base is weak
stronger acid +stronger base <—-> weaker acid+weaker base
stronger acid and weaker base are conjugate acid base pair.
stronger base and weaker acid are conjugate acid base pair.
Acid & Their Conjugate Base
Acid Conjugate Base
HCl Cl–
H2SO4 HSO4–
HNO3 NO3–
HSO4– SO4––
H3PO4 H2PO4–
HF F–
H2CO3 HCO3–
HCO3– CO3––
H2S HS–
HS– S––
H2PO4– HPO4––
HPO4– PO4––
H2O OH–
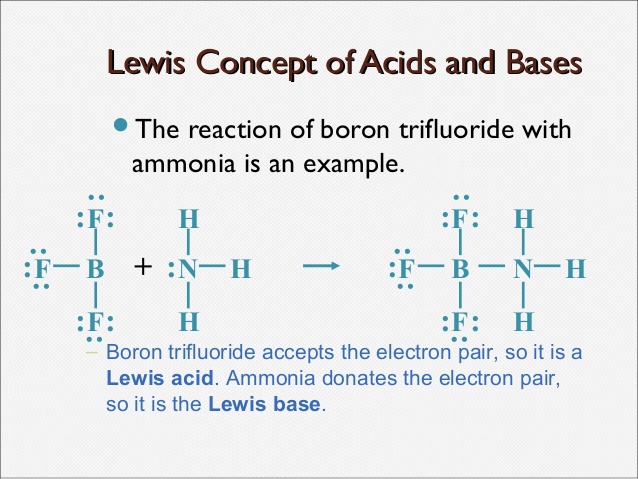
Lewis Concept–
a) Lewis Acid- Lewis Acid is electron pair acceptor
b) Lewis Base-Lewis base is electron pair donar
:NH3 + BF3 –> [H3N –> BF3]
e-pair e-pair
donar acceptors
(Lewis base) (Lewis acid)
c) Conditions for Lewis Acid-
i) Simple cation such as H+, Ag+, Fe++, Fe3+
2NH3 +Ag+ –> [H3N –> Ag <– NH3]+
ii) Compounds whose central atom has incomplete octet
Ex- BF3, BCl3, AlCl3, RMgX, MgCl2, etc.
iii) Compounds in which the Central atom has empty d-orbital or have orbitals of suitable energy & May extend their octet. Ex- SiF4, SiCl4
SiF4+2 F– –> [SiF6]2–
d) Conditions for Lewis base-
i) Molecules whose central atom has lone pair of electron
Such as : NH3 , :PH3,:PCl3, H2O:,ROH, ROR etc
ii) Negative ions or anions such as F–,Cl–,I–, etc
Definition of Hydroacids : Acid in which acidic H-atom is attached directly to other elements is called Hydroacid.
Definition of Oxyacids – Acid in which acidic H-atom is attached to central atom via an oxygen, acid is called oxyacid.
Some Important features of Acid & Bases
The oxides & hydroxides of alkali & alkaline earth metals are strong base & rest all are weak base. Basic nature increases on moving down the group.
Example.1 LiOH<NaOH<KOH<RbOH<CsOH
Example. 2 Be(OH)2<Mg(OH)2<Ca(OH)2<Sr(OH)2< Ba(OH)2
- Mineral acids such as H2SO4, HCl&HNO3 are strong acids.
- All organic acids (except those having –SO3H gr. i.e. Sulphonic acids) are weak acids.
- Acidic strength of oxy acid having same central atom increases with increases in oxidation number of central atom
Example.1
+1 +3 +5 +7
HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
very weak weak strong very strong
Example.2
+4 +6
H2SO3 < H2SO4
- Strength of oxy acid having different central atom but same oxidation state & same configuration increases with increase in electronegativity of central atom.
Example. 1. HOI+1<HOBr+1<HOCl+1
Example2. HIO4 < HBrO4 <HClO4
Example3. H3AsO4<H3PO4
- Strength of oxy acid increases from left to right in a period.
H2SiO4<H3PO4<H2SO4<HClO4
- The basicity of compound decreases from left to right among a period with increase in electronegativity.
Ex.NH3>H2O >HF
- The basicity of compound decreases from top to bottom in a group with increase in size of atom.