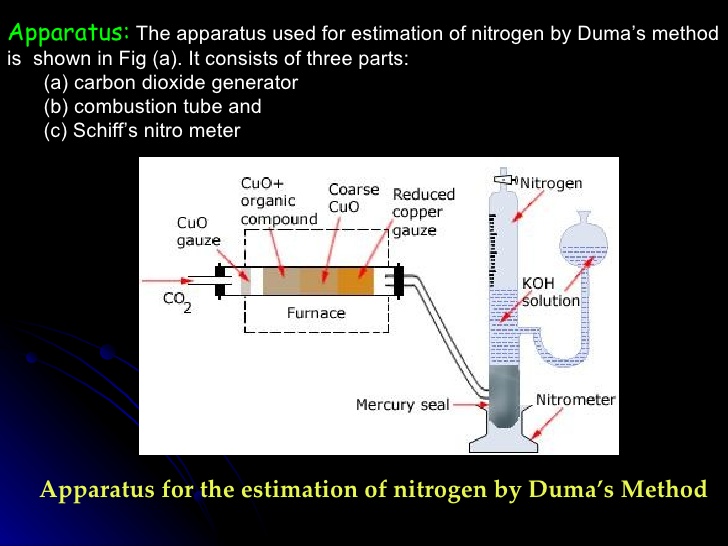
Duma & Kjeldahl’s Method : Nitrogen

source : slide player.com
Duma & Kjeldahl’s Method : Nitrogen
Estimation of Nitrogen- It is determined by two methods
- Duma’s Methods ( ii) Kjeldahl method
Duma’s Method
% of Nitrogen =[28 x volume of nitrogen at N.T.P x 100] / [22400 x weight of organic compound
volume at N.T.P. can be calculated as-
P1V1/T1 =P2 V2/ T2
At N.T.P.
V1=Vol. of N2 P2= 760 mm or 76cm
P1=Pressure of N2(mm) V2= ? Vol. of N2 at NTP
T1=Temp. of N2 T2= 273K
Numericals
- An organic Compound was analysed by Duma’s Method. 0.45 gm. of compd on combustion give 48.6 ml N2 at 270C & 756mm pressure. calculate % of N2.
Ans. At N.T.P.
P1=756 mm P2= 760 mm
V1=48.6 ml V2=? ml
T1=27+273= 300K T2= 273K
P1V1/T1 =P2 V2/ T2
( 756 X48.6)/300 =(760 x V2) /273
V2=43.99 ml
% of Nitrogen =[28 x volume of nitrogen at N.T.P x 100] / [22400 x weight of organic compound]
% of N2 = =[28 x 43.99x 100] / [22400 x 0.45]
% of N2 = 12.22%
(2) 0.2046 gm of an org. compd give 30.4ml of N2 at 150C and 732.7mm pressure. calculate the % of N2 (aq. Tension at 150C=12.75mm)
P1 = 732.7-12.75 = 719.95 mm P2 = 760 mm
V1= 30.4 ml V2= ?ml
T1 = 15+273=288k T2=273 k
P1V1/T1 =P2 V2/ T2
( 719.95 x 30.4)/288 = (760 x V2)/273
V2 =27.3 ml
% of Nitrogen =[28 x volume of nitrogen at N.T.P x 100] / [22400 x weight of organic compound]
=[28 x 27.3 x 100] / [22400 x 0.2046)
% of Nitrogen =16.68 %Ans.
Q. An org. Compd on analysis gave the following data-
- i) 0. 25 gm of organic compd on complete combustion gave 0.37 gm. of CO2 & 0.2 gm of H2O
- ii) 0. 25 gm. of organic compd on analysis by Duma’s Method gave 32 ml of N2 at N.T.P. Calculate % composition of org. Compd.
Solve. % of C=( 12 x 0.37 x 100) / (44 x 0.25) =40.36%
% of H=( 2 x 0.2 x 100) / (18 x 0,25 ) =8.89 %
% of Nitrogen =[28 x volume of nitrogen at N.T.P x 100] / [22400 x weight of organic compound]
% of Nitrogen =[28 x 32 x 100] / [22400 x 0.25] =16 %
% of O=100–(% of C+H+N)
% of O=100–(40.36+8.89+16) = 34.75% Ans.
Kjeldahl’s Method-
This method is based on the fact that many org. compd when heated with conc. H2SO4 in presence of CuSO4 & K2SO4. The Nitrogen is converted into (NH4)2SO4. The (NH4)2SO4 obtained is decomposed with caustic soda or caustic potash then NH3 is evolved which is passed into H2SO4 of known quantity & strength. The remaining unreacted H2SO4 is titrated against NaOH Solution of known strength. Hence % of N2 is then calculated
% of N2=[ 1.4 x normality of acid x volume of acid used with NH3] /weight of organic compound
% of N2 =( 1.4 x N x V)/w
- 0.2 gm of an org. compd was analysed by Kjeldahl’s method . NH3 evolved was absorbed in 60ml N/5 H2SO4. unused acid required 40ml N/10 NaOH for complete neutralisation find the % of N2
60 ml N/5 H2SO4 = 12 ml N H2SO4
40 ml N/10 NaOH=4ml N NaOH
Acid used with NH3= (12-4)
= 8 ml N H2SO4
% of N2 =( 1.4 x N x V)/w
% of N2 =( 1.4 x 1 x 8)/0.2 =56 % Ans.
- 0.788 gm. of an org. compd was analysed by Kjeldahl’s method. NH3 liberated was absorbed in 100 ml N H2SO4. Excess of H2SO4 is neutralised by 73.7 ml of N NaOH .Calculate % of N2= ?
Ans. Acid used with NH3 = (100-73.7) ml N H2SO4
= 26.3 ml N H2SO4
% of N2 =( 1.4 x 1 x 26.3)/0.788
% of N2= 46.72 %
- 1.029 gm of an organic compd on boiling with NaOH liberates some NH3, the complete neutralisation of which requires 14 ml of N/2 H2SO4 . Calculate % of N2=?
Ans. w=1.029 , V =14 ml
% of N2 =( 1.4 x N x V)/w
% of N2 =(1.4 x 0.5 x 14) /1.029
% of N2 =9.5 %