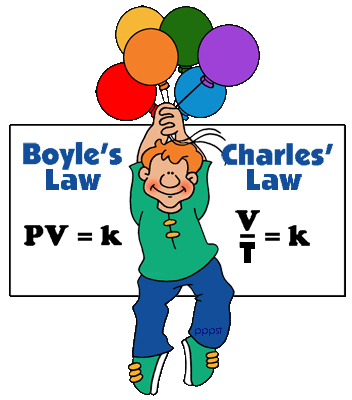GAS LAWS

source : youtube.com
- Boyle’s Law
This law was given by Boyle in 1662. According to this law,
At constant temperature, the volume of a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
V 1/P (when T =Constt.)
PV = CONSTANT
Boyle’s law can be derived by Kinetic Gas Equation
PV =1/3(mNv2) (i)
PV =(2/3). (1/3)(mNv2) (ii)
= 2/3 Ek
Ek = Average kinetic energy.
1/2 mNv2 T
1/2 mNv2 =KT (iii)
K is proportionality constt.
Compare Eq. (2) & (3)
PV = 2/3 KT
PV = constt.
V 1/P (At Constt. T) Boyle’s law
- Charle’s Law
This law was given by charles in 1787 According to this law,
At constant pressure, the volume of given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (T).
V T ( at constt. Pressure)
V =KT
V/T = constt.
If the volumes of given mass of a gas are V1 & V2 at constt pressure & absolute temperatures T1 & T2
According to Charle’s law-
V1/T1 = V2/T2
(Absolute Temperature = 273 + temperature in c)
- Avogadro’s Law
Berzelius presented a hypothesis & Avogadro modified, well tested & verified & then gave a law i-e Avogadro’s law.
According to this law,
‘Equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature & pressure contain equal number of molecules’.
For two gases, kinetic gas equation can be written as,
P1V1 =1/3 (m1 .N1 .v12) =2/3.1/3 .(m1 .N1 .v12)
P2V2 =1/3 (m2 .N2 .v22) =2/3.1/3 .(m2 .N2 .v22)
because, P1.V1 =P2.V2
1/2 m1. N1.v12 =1/2 (m2 .N2 .v22)
If temperature is constt, the average kinetic energy per molecule must be the same.
1/2 m1.v12 =1/2 m2.v22
N1 = N2 (Avogadro’s law.)
The important conclusions of this law-
- The proportion of volumes of gases in the gaseous reaction is the same as the proportion of their molecules or moles.
Ex. N2 + 3H2 —–.> 2NH3
one mole of N2 combines with 3 moles of H2 to produce 2 moles of NH3
According to Avogadro’s Law,
proportion of volumes of N2, H2 & NH3 in the reaction is 1:3:2
- The volume of 1 mole of gas at N.T.P. is 22.4 litres.
- Mass of 22.4 litre of any gas at N.T.P. is equal to its gram molecular weight.
Molecular weight = 2 × vapour density
Ex.- Mass of 22.4 litre of hydrogen at N.T.P. is 2 grams.