Order of reaction and molecularity-

source : SlidePlayer.com
Order of reaction –
“It is given by the number of atoms or molecules whose concentration changes during a chemical reaction.”
OR
“It is given by the number of concentration terms of atoms or molecules which determine the rate law.”
For ex.-
a) Reaction is said to be first order , if
r = dx / dt = KCA
b) Reaction is said to be second order , if
r = dx / dt = KCA2 or KCA.CB
c) Reaction is said to be third order , if
r = dx / dt = KCA3 or KCA2.CB or KCA.CB2
n1 A + n2 B + n3 D ——-> product
A , B and D are reactants
dx/dt = KCAn1 .CBn2.CDn3
K = constant
n = n1 + n2 + n3
n is order of rxn.
” Order of reaction may also be defined as , the sum of the powers to which the concentration terms of the reactants are raised in order to express the reaction rate.”
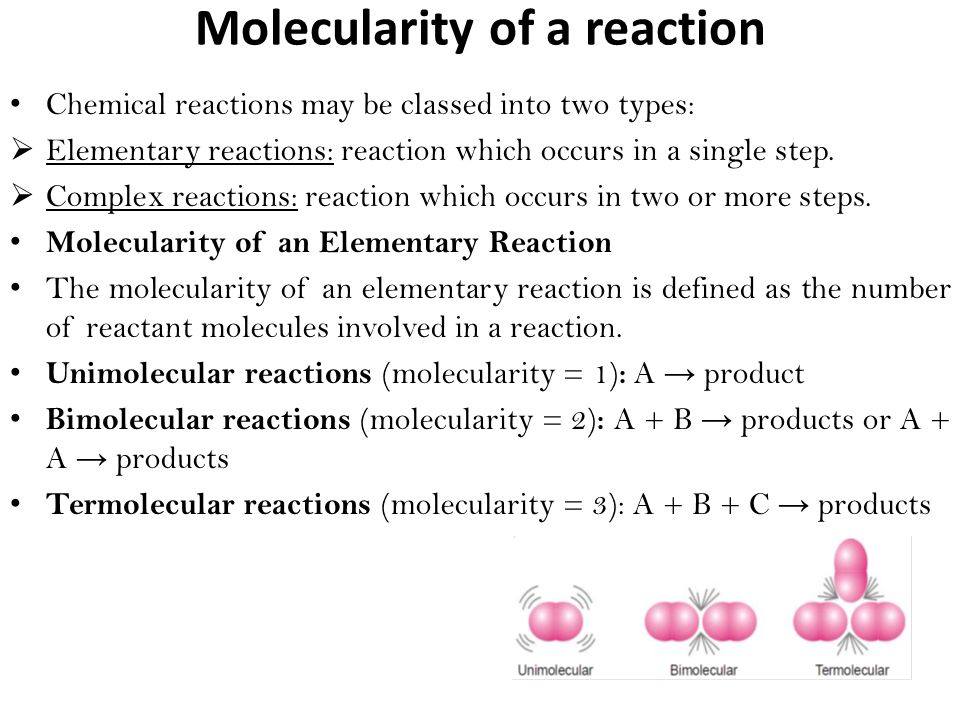
Molecularity-
” It is equal to the sum of the number of molecules of various reactants that take part in a chemical reaction as represented by a balanced chemical equation.”
If molecularity is one then reaction is unimolecular.
If molecularity is two & three then reaction is bimolecular and trimolecular or termolecular respectively.
Ex.1) Inversion of cane sugar-
C12H22O11 + H2O (excess) —————-> C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
order of rxn. = 1
molecularity = 2 (bimolecular)
Ex.2) Hydrolysis of methyl acetate-
CH3COOCH3 + H2O (excess) ————> CH3COOH + CH3OH
order of rxn. = 1
molecularity = 2 (bimolecular)
Difference between order of reaction and molecularity-
Order of reaction –
1) “It may also be defined as , the sum of the powers to which the concentration terms of the reactants are raised in order to express the reaction rate.”
2)It may be whole number , zero or fractional value .
3) It is determined experimentally , it is determined by rate for overall reaction.
4) It can be obtained from a balanced chemical equation.
Molecularity-
1) ” It is equal to the sum of the number of molecules of various reactants that take part in a chemical reaction as represented by a balanced chemical equation.”
2) It is always a whole number.
3) It is a theoretical concept , it depends upon the rate determining step in the reaction mechanism.
4) It is obtained from a balanced chemical equation.