Plaster – Paris

source : indian express.com
Plaster of Paris [ (Ca SO4)2 . H2O]
or
Calcium sulphate hemihydrate CaSo4 . 1/2 H2O
Methods of preparation:
From Gypsum — When gypsum is heated at 120 degree C to 130 degree C , plaster of paris is obtained.
2(CaSo4 . 2H2O) ——-> (CaSo4)2 . H2o + 3H2O
Properties:
- It is white powder, sparingly soluble in water.
- Effect of heat: At 200 degree C anhydrous calcium sulphate is obtained. At 1200 degree C it decomposes.
[(CaSo4)2.H2O] ——–> 2 CaSo4 + H2O
2[ CaSo4] ——-> 2 Cao + 2So2 + O2
3. Reaction with water: Gypsum is obtained which sets as hard mass. This process is called setting of plaster of paris.
(CaSo4)2 . H2O +3H2O ——-> 2[CaSo4.2H2O]
Uses:
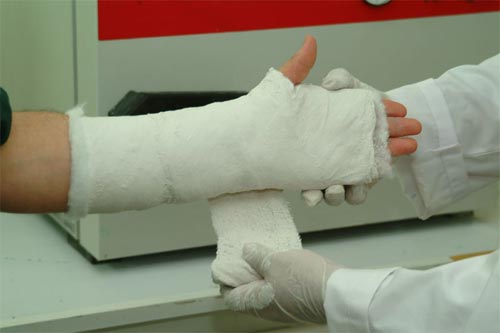
a) for setting dislocated or broken bones.
b) In making chalks.
c) For making toys and statues.
Conversions:
-
(Barium sulphate to barium chloride:
BaSO4 +4C(coke) ——–>BaS(barium sulphide) + 4CO( carbon monoxide)
BaS + 2HCl ——–> BaCl2 + H2S
-
Calcium sulphate to Calcium chloride:
CaSO4 + 4C ——–> CaS + 4CO
CaS + 2HCl ——–> CaCl2 + H2S
-
Barium sulphate to Barium nitrate:
BaSO4 + 4C ——–> BaS + 4CO
BaS + 2 HNO3 ———> Ba (NO3)2 + H2S
-
Hydrated magnesium chloride to magnesium oxide:
MgCl2 . 6H2O——-> Mg( OH)Cl + HCl + 5H2O
Mg(OH)Cl ———> Mgo + HCl
-
Hydrated magnesium chloride to anhydrous magnesium chloride:
MgCl2 . 6H2O ——–> Mg(OH)Cl + HCl + 5H2O
Mg(OH)Cl + HCl(dry gas) ——–> MgCl2 + H2O
-
Barium nitrate to Barium chloride:
Ba(NO3)2 ——–> BaO + NO2 + O2
BaO + 2HCl ——–> BaCl2 + H2O
-
Barium nitrate to Barium sulphate
Ba (NO3)2 ———> BaO + NO2 + O2
BaO+ H2SO4 ———> BaSO4 + H2O
Read more articles at chemistryonline.guru