Average & half life

source : www.nde-ed.org
Average Life Period & half life period-
Half Life Period-
“It is equal to the time required to disintegrate half of the quantity of the radioactive element taken”.
or
“Half life period is the time during which half of the quantity of a sample of radioactive element disintegrates.”
Half life is represented by t1/2. The value of t1/2 does not depend upon temperature, pressure, catalyst and mass of radioactive substance taken etc.
t1/2 is a measure of radioactivity and stability of radioactive element. Greater is the value of t1/2, greater is the stability of the radioactive element & smaller is its radioactivity.
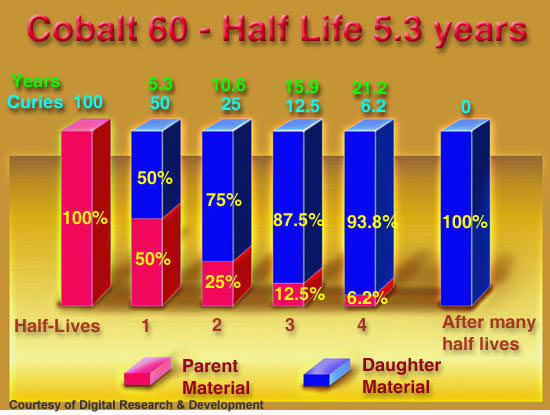
Ex.- Half life of Ra226 is 1580 years. This shows that after 1580 years, the mass of radium is half of the mass taken.
After 2×1580 (=3160 year) the quantity of Ra226 left will be ¼ ( one fourth) of the mass taken.
Suppose initial mass or no. of atoms of a radioactive element is No. its half life period is t1/2
After one t1/2atoms left = No/2
Atoms left after two half lives = No/4=No/22
After three half lives atoms left= No/8 = No/23
Atoms left after ‘n’ half lives= No/2n
The mass or no. of atoms left after ‘n’ half lives is ‘N’
N= No(1/2)n
T=n×t1/2
Relation between disintegration constant and half life-
Radioactive disintegration is 1st order reaction . for First order Reaction,
K = ( 2.303 / t ) log a /(a- x)
If t= t1/2 , & x = a/2 then,
K = ( 2.303 / t1/2 ) log a /(a- a/2)
K = ( 2.303 / t1/2 ) log 2
because , log2 = 0.3010
K = ( 2.303 x 0.3010 / t1/2 )
K = 0.693 / t1/2
Average Life Period-
“Reciprocal of t1/2 of a radioactive element is called its average life period.”
It is represented by τ (Tau)
τ =1/K
K= 0.693 /t1/2
K = t1/2 / 0.693