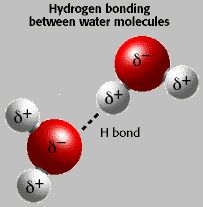
Hydrogen bond

source : www.Chemhume.co.uk
When Hydrogen atom is covalently bonded with a highly electronegative element then it has the tendency to form bond with other electronegative element. This type of bond is called Hydrogen bond. It is represented by dotted lines .(…)
Ex- 
Types of hydrogen bond :
(A) Intermolecular Hydrogen bond :
When H- bond is formed between two or more molecules of same or different compounds then it is called Intermolecular Hydrogen bond.
Example: H2O, HF, NH3, glycerol,phenol , amino acid , alcohol etc.

(B) Intramolecular Hydrogen bond :
When H- bond is formed within the atoms of a molecule then it is called Intra molecular H- bond.
Example: o-fluorophenol , o-hydroxy benzoic acid, o-nitro phenol etc.
Nature of hydrogen bond :
When hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to more electro negative elements as such F,N,O, the bond is polar, So H-atom acquires partial positive charge and hence it has tendency to form bond with other electronegative atom. Hence H- bond is electrostatic in nature. It is a weak bond.
Conditions for H- bond formation :
Hydrogen bond is formed with atoms of small size like F,N,O. These (F,N,O) form H-bond due to the small size. H-bond is formed with elements having high value of electro negativity.
Effect of H-bond on physical properties of compounds :
1) Water is liquid at room temperature , while H2S (Hydrogen sulphide ) is a gas.
Reason – Water molecules are associated through inter molecular H- bond .So molecules become closer to each other while in H2S , hydrogen bond is not present. So water is a liquid and H2S is a gas.

2. Boiling point of ammonia (NH3 ) is greater than phosphine.
Reason- Ammonia molecules are associated through inter molecular H- bond .So molecules become closer to each other & more amount of energy is required to break these forces . while in phosphine H- bond is not present.
source : Socratic