Isotonic solution-

source : slideplayer.com
Isotonic or Iso – osmotic solutions-
Two solutions of different substances having same osmotic pressure at same temperature are called isotonic solutions. When isotonic solutions are separated by Semipermeable membrane , no osmosis takes place. Isotonic solutions have equal molar concentrations.
For isotonic solutions,
π1 = π2
π1 and π2 are osmotic pressures.
C1 = C2
C1 and C2 are molar concentrations
[ C = n/V = no. of moles /volume of solution in litre ]
n1 /V1 = n2 / V2 [ n = w /m = weight of solute / molecular weight ]
w1 / m1 V1 = w2 / m2 V2
These are applicable when there is no dissociation or association of solute takes place.
(i) In case of isotonic solution of non electrolyte solutes ( ex. isotonic solutions of urea and glucose ),
π1 = π2
C1 = C2
(ii)In case of isotonic solution of urea (non electrolyte ) and NaCl ( electrolyte it dissociates in solution) ,
π1 = π2
C1 ≠ C2
(iii) In case of isotonic solution of urea (non electrolyte ) and Benzoic acid ( electrolyte it associates in solution) ,
π1 = π2
C1 ≠ C2
Hypotonic solution-
If a solution having less osmotic pressure than other is called hypotonic solution .
or
Solution is hypotonic if it has less solute and more water than another solution.

source : Your Nursing Tutor
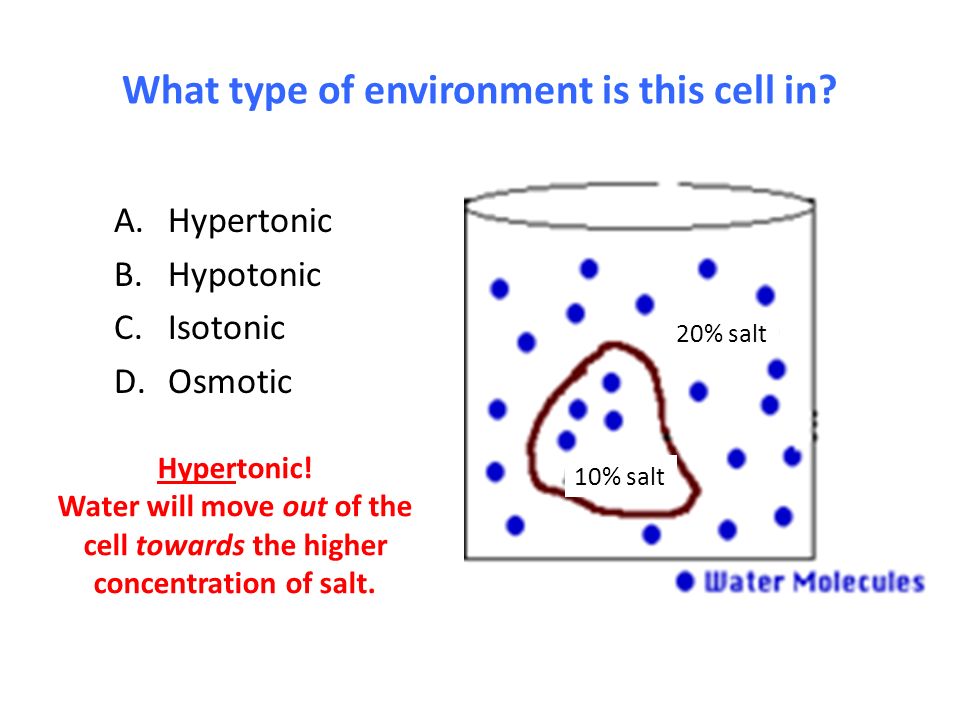
Hypertonic solution-
If a solution having more osmotic pressure than other is called hypertonic solution.
or
When a solution has more solute per litre than another is called hypertonic solution.