Law of Gaseous volumes and Avogadro law

source : ncerthelp.com

source :slideplayer.com
Law of gaseous volumes-
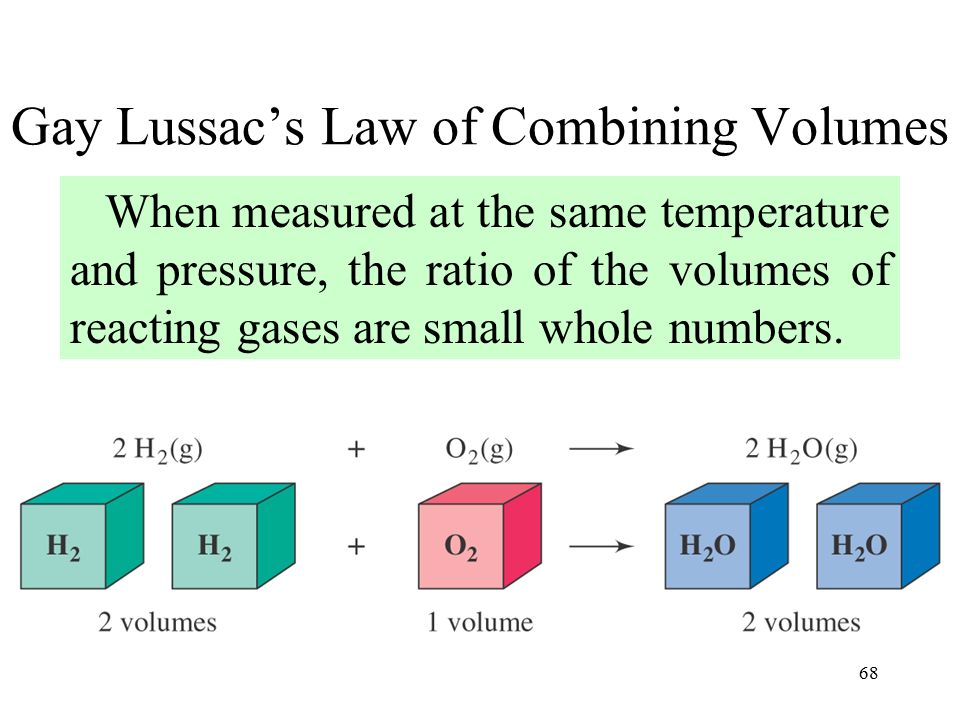
This law was given by Gay Lussac. According to this law,
” When gases combine they do so in volumes which bear a simple ratio to each other and also to the product formed provided all gases are measured under similar conditions of temperature and pressure . “
Ex.1 –
H2 + Cl2 = 2HCl
1 Vol. 1 vol. 2 vol.
Ratio 1 : 1 : 2
Ex.2-
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O
2 Vol. 1 vol. 2 vol.
Ratio 2 : 1 : 2
Ex.3-
N2 + 3H2 = 2 NH3
1 Vol. 3 vol. 2 vol.
Ratio 1 : 3 : 2
Question ) 8.0 litre of H2 and 6.0 litre of Cl2 are allowed to react to maximum possible extent . Find out volume of reaction mixture . Suppose pressure and temperature remains constant through out the experiment.
Solution )
H2 + Cl2 ——-> 2 HCl
Volume before reaction 8 litre 6 litre 0
Volume after reaction 2 litre 0 litre 12 litre
Total volume after reaction = volume of H2 left + volume of HCl formed = 2 + 12
Volume of reaction mixture = 14 litre Ans.
Avogadro’s Law-
According to this law,
“Equal volumes of gases under similar conditions of pressure and temperatures possess equal number of moles or molecules.”
V ∝ n at constant pressure and temperature
V ∝ N at constant pressure and temperature
n is number of moles and N is number of molecules of gases in volume ‘V’ at pressure ‘P’ and temperature ‘T’.
” At one atmosphere pressure and 00C or 273 K , one mole of gas contains 6.023 x 10 23 ( avogadro’s number ) molecules of gas. “