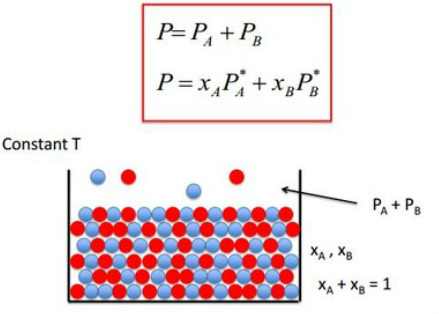
Raoult’s law-
source : sites.google.com
Raoult’s law-
Question 1) At 300 K , the vapour pressure of an ideal solution containing one mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550 mm. At the same temperature if one mole of B is added to the solution , the vapour pressure of solution increases by 10 mm Hg. Calculate the vapour pressure of A and B in their respective pure state ?
Solution)
Initially,
PM =550 mm, PA0 = ? , PB0 =?, nA = 1 , nB = 3
PM = PA0.XA + PB0.XB
= PA0 [nA/(nA + nB)] + PB0 [nB/(nA + nB)]
550 = PA0 [1/(1 + 3)] + PB0 [3 /(1 + 3)]
550 = ( PA0/4 ) + ( 3PB0/ 4)
550 x 4 = PA0 + 3PB0
PA0 + 3PB0 =2200 ——– eq.1
On addition of one mole of B,
nA = 1 , nB = 3+1 = 4
The vapour pressure of solution increases by 10 mm Hg . Thus ,
PM =550 + 10 = 560 mm
PM = PA0.XA + PB0.XB
= PA0 [nA/(nA + nB)] + PB0 [nB/(nA + nB)]
560 = PA0 [1/(1 + 4)] + PB0 [4 /(1 + 4)]
560 = ( PA0/5 ) + ( 4 PB0/ 5)
560 x 5 = PA0 + 4PB0
PA0 + 4 PB0 =2800 ——– eq. 2
PA0 + 3 PB0 =2200
PA0 + 4 PB0 =2800
By Subtracting ,
– PB0 =-600
PB0 = 600 mm Ans.
putting the value of PB0 in eq. 1
PA0 + 3 x 600 = 2200
PA0 = 2200 – 1800 = 400 mm
PA0 = 400 mm Ans.
Question 2) 0.1 M solution of glucose was found to be isotonic with a solution of X in 100 gm water. Calculate relative lowering in vapour pressure of solution of X in water ?
Solution )
0.1 M solution of glucose is isotonic with solution of X in 100 gm water.
Therefore , concentration of solution of X = 0.1 M
It means 0.1 mole of X in 1000 ml or one litre of solution.
For dilute solution ,
volume of solution = volume of solvent (water) = weight of water( = v x d = 1000 x 1= 1000 gm)
W = 1000 gm , M of water = 18
mole of X ‘n’= 0.1, mole of water ‘N’ =W/M = 1000/18
According to Raoult’s law
po – ps / po = (n /n +N )
= 0.1 / [ 0.1 + (1000/18)]
Relative lowering of vapour pressure = po – ps / po = 0.0018 Ans.
Question 3) What weight of solute ( molecular weight =60) is required to dissolve in 180 gm of water to reduce the vapour pressure to 4/5th of pure water ?
Solution )
ps = 4/5 po , w = ? , m = 60 , W = 180 gm , M of water = 18
According to Raoult’s law
(po-ps) /po =wM/Wm
[po– (4po /5) /po] = w x 18 /180 x 60
(5 po – 4 po) /5 po = w /10 x 60
1 /5 = w / 600
w = 600 /5 = 120
w = 120 gm.
Question 4 ) A mixture of ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapour pressure of 290 mm at 27 0C.When mole fraction of ethyl alcohol is 0.65. Calculate the vapour pressure of ethyl alcohol, if vapour pressure of propyl alcohol is 210 mm.
Solution )
PM = 290 mm , PoC2H5OH= ? ,
PM = PoC2H5OH.XoC2H5OH+ PoC3H7OH.XoC3H7OH
X C2H5OH = 0.65 , XC3H7OH = 1 – 0.65 = 0.35 , PoC3H7OH = 210 mm
290 = PoC2H5OH x 0.65 + 0.35 x 210
290 = PoC2H5OH x 0.65 + 73.5
290 – 73.5 = PoC2H5OH x 0.65
PoC2H5OH = 216.5 / 0.65 = 333.07