Born – Haber cycle

source: curvetube.com
Born – Haber cycle-
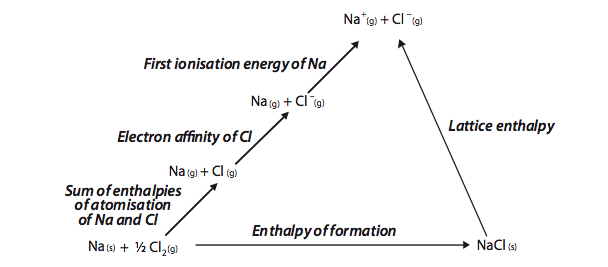
Max Born and Fritz Haber proposed a thermodynamic cycle which relates the lattice energy of crystal to the other thermochemical data such as sublimation energy ( the energy required to convert solid metal ion to gaseous atom , denoted by (ΔHsub ), dissociation energy ( the energy required to convert gaseous molecule to gaseous atom , denoted by D), ionisation energy(I),electron affinity(E) and heat of formation of crystal (H). This cycle is known as ‘Born Haber cycle’.
The energy terms involved in building a crystal lattice such as sodium chloride may be taken in steps the elements in their standard state are converted to gaseous atoms ,then to ions and finally converted into crystal lattice .
Na(s) + 1/2 Cl2(g) ————-> NaCl (s)
The overall process takes place in following steps-
i) Conversion of metallic sodium into gaseous sodium atoms-
First of all solid sodium atom is converted into gaseous state . The energy required for the conversion of one mole of solid sodium to gaseous sodium is called enthalpy of sublimation (ΔH sub).
Na(s) + ΔH sub ———> Na(g)
ii) Dissociation of chlorine molecules into chlorine atoms-
The energy required to convert gaseous chlorine molecule to atoms is called enthalpy of dissociation(D).
1/2 Cl2 (g) + D/2 ——-> Cl(g)
iii) Conversion of gaseous sodium atom into sodium ion –
The amount of energy required to convert one mole of gaseous sodium atom into sodium ion in gaseous state is called ionisation energy .
Na(g) + IE ——–> Na+ (g) + e–
iv) Conversion of gaseous chlorine atom into gaseous chloride ion –
The amount energy released during the conversion of one mole of gaseous chlorine atom into gaseous chloride ion is known as electron gain enthalpy and represented by EA .
Cl(g) + e ———–> Cl– (g) +EA
v) Combination of oppositely charged ions to form a solid crystal-
Na+ and Cl– attract each other and form solid NaCl crystal. The amount of energy released when one mole of solid crystalline compound is obtained from gaseous ions is called lattice energy(U).
Na+ (g) + Cl– (g) ———> NaCl (s) + U
The total reaction is,
Na(s) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) ————-> NaCl (s)
The enthalpy change for the above reaction is called enthalpy of formation(ΔfH).

source: chemistry
These steps are represented in the form of ‘Born – Haber cycle’.
Δ H f 0 = ΔH sub + D/2 + IE + EA +U
Applications of Born – Haber cycle-
i) It can be used to determine electron gain enthalpy , ionisation energy and lattice energy.
ii) It can be used to explain the stability of molecules.